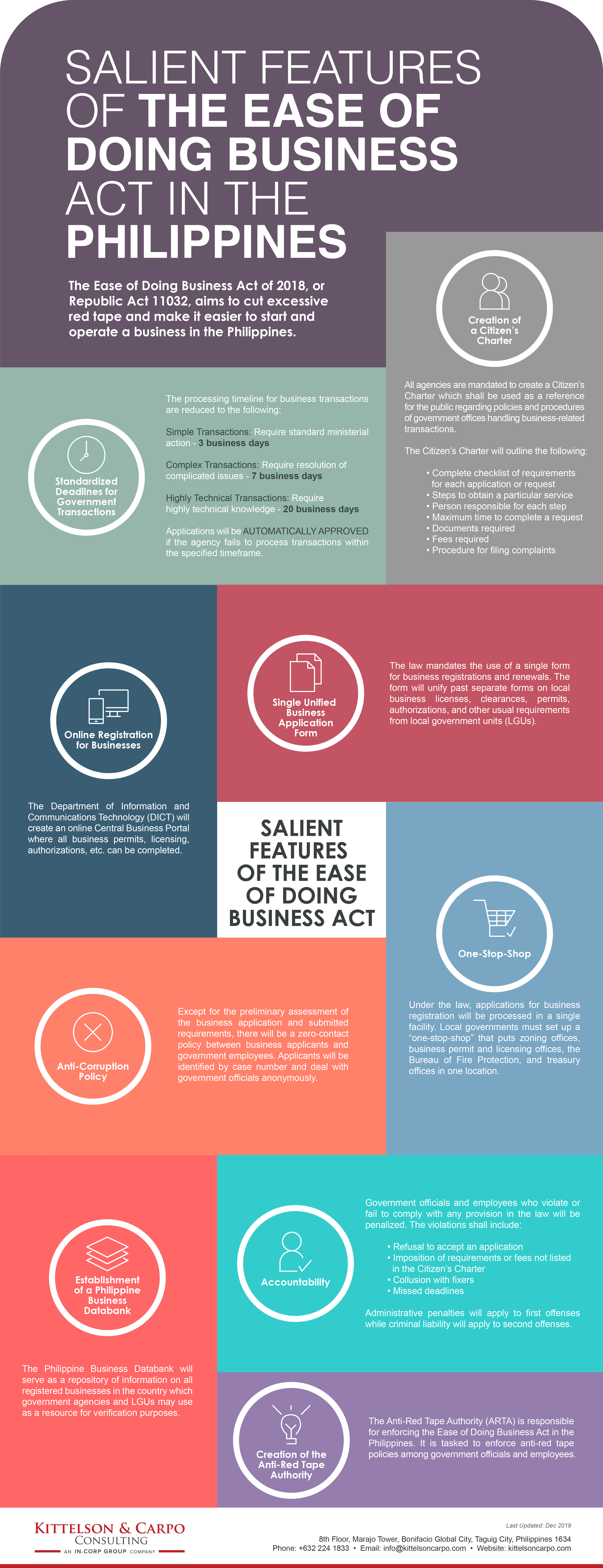
Salient Features of the Ease of Doing Business Act in the Philippines [Infographic]
The Ease of Doing Business Act of 2018, or Republic Act 11032, aims to cut excessive red tape and make it easier to start and operate a business in the Philippines.
Salient Features of the Law
Single Unified Business Application Form
The law mandates the use of a single form for business registrations and renewals. The form will unify past separate forms on local business licenses, clearances, permits, authorizations, and other usual requirements from local government units (LGUs).
One-Stop-Shop
Under the law, applications for business registration will be processed in a single facility. Local governments must set up a “one-stop-shop” that puts zoning offices, business permit and licensing offices, the Bureau of Fire Protection, and treasury offices in one location.
Online Registration for Businesses
The Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) will create an online Central Business Portal where all business permits, licensing, authorizations, etc. can be completed.
Standardized Deadlines for Government Transactions
The processing timeline for business transactions are reduced to the following:
- Simple Transactions: Require standard ministerial action – 3 business days
- Complex Transactions: Require resolution of complicated issues – 7 business days
- Highly Technical Transactions: Require highly technical knowledge – 20 business days
Applications will be AUTOMATICALLY APPROVED if the agency fails to process transactions within the specified timeframe.
Creation of a Citizen’s Charter
All agencies are mandated to create a Citizen’s Charter which shall be used as a reference for the public regarding policies and procedures of government offices handling business-related transactions.
The Citizen’s Charter will outline the following:
- Complete checklist of requirements for each application or request
- Steps to obtain a particular service
- Person responsible for each step
- Maximum time to complete a request
- Documents required
- Fees required
- Procedure for filing complaints
Anti-Corruption Policy
Except for the preliminary assessment of the business application and submitted requirements, there will be a zero-contact policy between business applicants and government employees. Applicants will be identified by case number and deal with government officials anonymously.
Establishment of a Philippine Business Databank
The Philippine Business Databank will serve as a repository of information on all registered businesses in the country which government agencies and LGUs may use as a resource for verification purposes.
Accountability
Government officials and employees who violate or fail to comply with any provision in the law will be penalized. The violations shall include:
- Refusal to accept an application
- Imposition of requirements or fees not listed in the Citizen’s Charter
- Collusion with fixers
- Missed deadlines
Administrative penalties will apply to first offenses while criminal liability will apply to second offenses.
Creation of the Anti-Red Tape Authority
The Anti-Red Tape Authority (ARTA) is responsible for enforcing the Ease of Doing Business Act in the Philippines. It is tasked to enforce anti-red tape policies among government officials and employees.
